The term osteochondrosis itself comes from two words: osteo - bone and chondrue - cartilage. Simply put, it is the ossification of cartilage. Although this interpretation is fundamentally wrong. Some go even further in their delusions and are confident that osteochondrosis means joint deposition of salts. Moreover, it is table salt that is said to be consumed in large quantities for food.
Pathogenesis
In reality, everything happens a little differently. And harder. And table salt, if it plays any role in the occurrence of osteochondrosis, is very indirect. Osteochondrosis is based on degeneration and degeneration of articular cartilage. It is not a disease in itself, but a pathological process that can be observed almost everywhere where there is connective cartilage tissue.
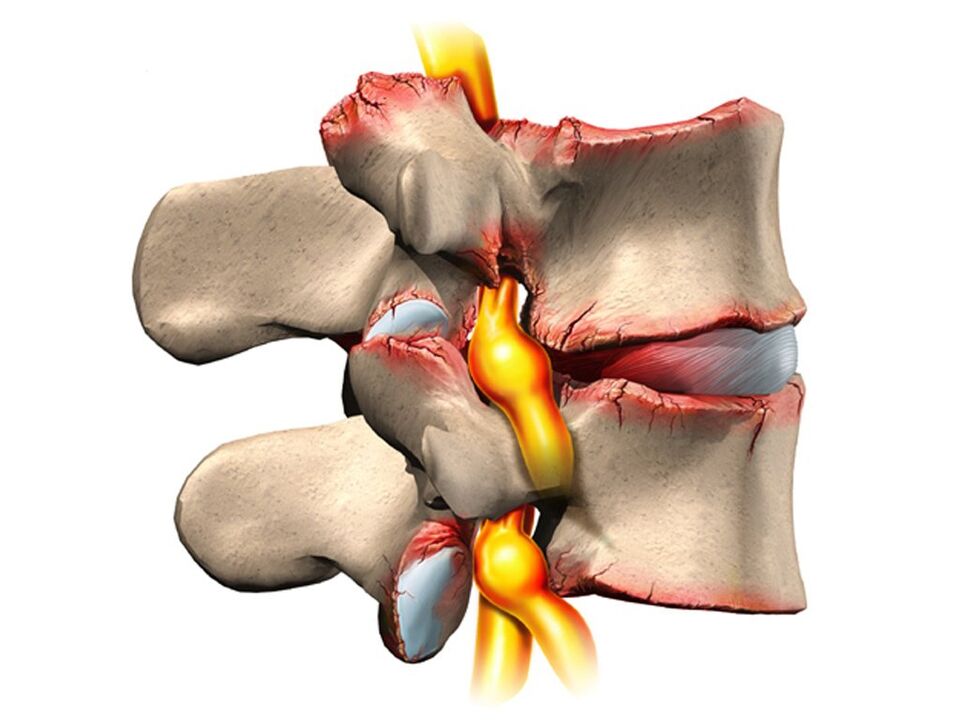
Nevertheless, osteochondrosis mainly affects the spine. Why is that? The situation is that there is a kind of pillow between the vertebrae - intervertebral (intervertebral) plates. The role of these cartilage discs is to cushion and protect the vertebral bodies from premature wear due to mechanical stress. The disc consists of an inner liquid nucleus pulposus surrounded by an annulus fibrosus and an upper and lower end plate.
The plate is subjected to enormous mechanical stress, which leads to permanent damage to its cellular structures. In humans, these processes are too stressful - this is our pay for straight walking. In order for a disk not to be completely "erased", it must constantly regenerate, that is, rebuild itself. The balance of damage-regeneration processes determines the normal structure of the intervertebral disc. Another interesting detail is that the supply of blood and nutrients to the discs does not occur through the overgrown blood vessels in childhood, but in a diffuse way, from the bone tissue of the vertebral bodies. Again, pay for the ability to move two, not four limbs.
Because of this, intervertebral discs are easily damaged anatomically and physiologically. Any negative process in the body leads to upset damage-regeneration balance, dystrophy and degeneration of the discs. A structurally defective disc can no longer withstand the proper mechanical stress. Excessive pressure exerted by the cover vertebrae causes the cartilage discs to move in different directions, usually sideways and backward. This process is called disc herniation.
The bone tissue of the vertebrae that has lost its cartilage lining also undergoes mechanical wear. Permanent trauma to the anterior edge of the vertebral bodies results in abnormal bone growth - osteophytes. Spondylosis develops. Due to the degeneration and displacement of the disc, the intervertebral spaces are reduced, the spinal canal is narrowed, and the roots of the spinal nerves are damaged in the so-called foraminal cavities.
Cause
The causes or etiological factors of osteochondrosis are varied. They can be local, i. e. , due to the pathology of the spine itself, and they can also be general disorders at the organizational level. Any pathology that leads to damage to the structure of the spine or metabolic disorders can be considered a cause of osteochondrosis. In this regard, they are:
- Changes in the configuration of the spine (scoliosis, pathological lordosis or kyphosis).
- Other defects of the musculoskeletal system are flat legs, narrow shoulder girdle, anomalies in the structure of the pelvis.
- Spine injury.
- Weak immunity.
- Metabolic disorders - osteoporosis, obesity, diabetes mellitus, thyroid disease.
- Cardiovascular diseases - atherosclerosis, high blood pressure.
- Indigestion that leads to insufficient absorption of nutrients from the gastrointestinal tract.
- Heredity.
It should be noted that the above pathological conditions do not necessarily lead to osteochondrosis. This requires constant exposure to certain predisposing factors - hypothermia, malnutrition, sedentary lifestyle, or, conversely, excessive physical exertion.
Symptoms
Osteochondrosis itself is an asymptomatic process. However, signs of intervertebral disc degeneration are varied. How come? The fact that the clinical manifestations of osteochondrosis are based on complications - disc herniation, spondylosis, sciatica, spinal stenosis.
In addition, the clinic varies greatly depending on the dominant localization of the process in the cervical, thoracic, or lumbosacral spine. The last stage is most often affected, as the lower back absorbs maximum physical activity. Signs of osteochondrosis of the lumbosacral region:
- Pain (lumbodynia, lumbago, sciatica).
- Restriction of movement in the lower back and lower extremities (intermittent claudication).
- Here are the sensitivity disorders of the type of paresthesia - numbness, burning, creep.
- Abnormal tension in the lumbar muscles.
- Disorders of pelvic organs in the absence of treatment.
Cervical osteochondrosis is slightly less common than lumbosacral. However, this pathology is quite common. In addition to pain (cervicalgia), decreased sensitivity, and movement of the upper limbs, cervical osteochondrosis due to a disruption of the blood supply to the brain also has its own characteristics. These qualities are manifested in:
- Insomnia.
- Headache, dizziness.
- Periodic nausea.
- General weakness, rapid fatigue.
- Fluctuations in blood pressure.
- Occasionally a toothache.
- Behavioral reactions in the form of tearing, irritability.
The thoracic region of osteochondrosis is relatively rarely affected. Patients in this case are people who sit in a fixed, uncomfortable position because of their occupation - students, schoolchildren, programmers, office workers. Symptoms of osteochondrosis in this case include:
- Chest pain and paraesthesia.
- Shortness of breath.
- Feeling of a heartbeat.
- Restriction of movement in the chest spine.
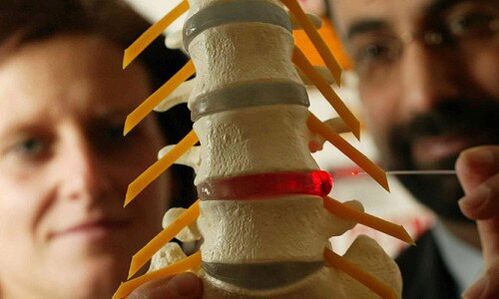
Diagnostics
From all this, it is clear that osteochondrosis is a chameleon disease. Due to the similarity of the signs, it can be easily confused with cerebral vascular catastrophe, hypertension, myocardial infarction, angina pectoris, neurotic disorders. Therefore, to make a correct diagnosis, a comprehensive complex diagnosis is needed to correctly define the symptoms and treatment of osteochondrosis.
In addition to the traditional questioning and clarification of patient complaints, this diagnosis should include medical examination and special research methods. These methods include x-ray of the spine, ultrasound of the internal organs. Recently, computer and magnetic resonance imaging have been successfully used to diagnose osteochondrosis.
Treatment
Therapeutic tactics for osteochondrosis include:
- Medicines.
- Massage.
- Physiotherapy procedures.
- Physiotherapy (gymnastics).
- Manual therapy.
- Acupuncture.
Medication for osteochondrosis is primarily aimed at relieving pain and eliminating inflammatory processes in the nerve roots. In various combinations, these drugs are widely used in the form of ointments, injections, tablets for the treatment of osteochondrosis. It should be borne in mind that these drugs have a negative effect on the liver, stomach and intestines. This can exacerbate metabolic disorders in osteochondrosis. Local anesthetics are good for relieving the pain of blockade. True, the effects of these funds are short-lived and do not affect osteochondrosis as a whole in any way.
Metabolic processes can be improved locally and at the body level with the help of drugs such as chondroprotectors, immunostimulants, minerals with vitamins. Chondroprotectors are used in tablets, ointments and ampoules. Strengtheners include vitamin C, group B, in combination with minerals. In this regard, calcium formulations are most preferred. In fact, contrary to some misconceptions, osteochondrosis is not based on excess, but only on calcium deficiency.
After successful alleviation of exacerbation, physiotherapy procedures, massage and practical therapy are presented. Physical methods include calcium electrophoresis, hydrocortisone phonophoresis, amplification, and paraffin therapy. All of these measures are designed to eliminate pain and inflammation in the nerve roots, ligaments, and muscles. Massage for osteochondrosis is performed according to the generally accepted method. The massage zone is selected depending on the location of the osteochondrosis. The expansion of the range of motion is achieved with the help of motion therapy. Initially, there is virtually no dynamic load in the exacerbation phase. The patient is in an optimal posture at all times. At this time, it is desirable to wear immobilizing devices - lumbar corset, Shants neck collar. As exacerbation passes, the amount and duration of movements during training therapy increases.
Recently, non-traditional methods of treatment have been used to treat osteochondrosis - acupuncture, manual therapy, osteopathy. Acupuncture has an effect on special biologically active points located along the spine, earlobes, hands and feet. With manual therapy, the normal position of the vertebrae and intervertebral discs is restored by manual intervention by a specialist. In osteopathy, special techniques are used to ensure the structural integrity of the locomotor system. In the absence of the effect of conservative measures for the treatment of osteochondrosis, lasting pain, complications and surgery are required. The abnormally displaced plate is removed. A microdiscectomy is currently being performed for this purpose - endoscopic removal of the displaced plate.